
Skills, tasks and salary of the Big Data specialist, the true interpreter of the data economy and data-driven business. Here's how to become a Data Scientist and what the career outlets are.
he Data Scientist is the true interpreter of the data economy and data-driven business. In fact, that of the Data Scientist is one of the most "in" roles in the digital economy, listed by the World Economic Forum as one of the 21 professions for which business demand will continue to increase until at least 2022. Even Harvard Business Review has called this profession "the sexiest job of the 21st century."
In collaboration with domyprogramming.org that helped me to do my programming homework
What does Data Scientist do?
The Data Scientist's job is to know how to manage Big Data (big data, both structured and unstructured) and derive useful insights from it for the business and success of the organization he or she works for.
This is a highly specialized figure with training that often goes beyond a master's degree, because skills range from in-depth knowledge of data mining and data analysis software, statistical methods and predictive models, and visualization tools; he or she must, in addition, be equipped with "soft skills" such as curiosity, clear communication, problem solving, and teamwork.
The role of the Data Scientist is enhanced by the spread of technologies such as Analytics, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), which help top management make targeted decisions.
What is Data Science
Data science or data science is the set of methodological principles and multidisciplinary techniques that aims to interpret and extract knowledge from data, through the analysis of an expert, the Data Scientist.
The term "data science" was first used in 1974 by Danish computer scientist Peter Naur in his book Concise Survey of Computer Methods. Understood as a discipline concerned with the management and manipulation of data (in those days there was still no reference to the fact that valuable information could be extracted from data), the new term was a further evolution of the concept of "datalogy," which Naur had coined a few years earlier to find an alternative to the generic term "computer science." Recognition of data science as a distinct discipline from computer science and statistics came in 2006 with the definition of the 6 fields of expertise by an American computer scientist and professor of statistics and computer science at Purdue University, William Cleveland: multidisciplinary research, models, data processing, pedagogy, tool evaluation, and theory.
The skills of a Data Scientist
The Data Scientist must combine the technical skills and intuition to organize large data sets and answer complex questions, producing reports that help top managers strategize. He or she must be able to navigate both structured (organized by category, such as sales data) and unstructured (more difficult to classify in an automated way, such as social media comments) data by conducting quantitative and qualitative analysis.
Attention also needs to be paid to more innovative and specialized skills such as data wrangling or munging, which allows starting from raw data (raw data) and transforming it into data that is homogeneous in format, capable of being brought into the Analytics process.
Finally, you need soft skills depending on the industry in which you work: the skills needed in marketing are different from those for PA or the Tlc industry. This was pointed out by the research firm Gartner already in a 2016 study, where it called the Data Scientist's preparation "multidisciplinary" as it falls between the macro areas of statistics, coding, traditional research, data engineering, Machine Learning and marketing. These in turn expand into more specific disciplines such as data preparation and governance, SQL, predictive analytics, advanced mathematics, statistical modeling, metrics definition, customer understanding, and translation of results into non-technical language.
In particular, data science is based on techniques that bring together different disciplines: ranging from mathematics to statistics, from information science to computer science. Then there are subfields that are increasingly emerging, among them such as data visualization and business intelligence.
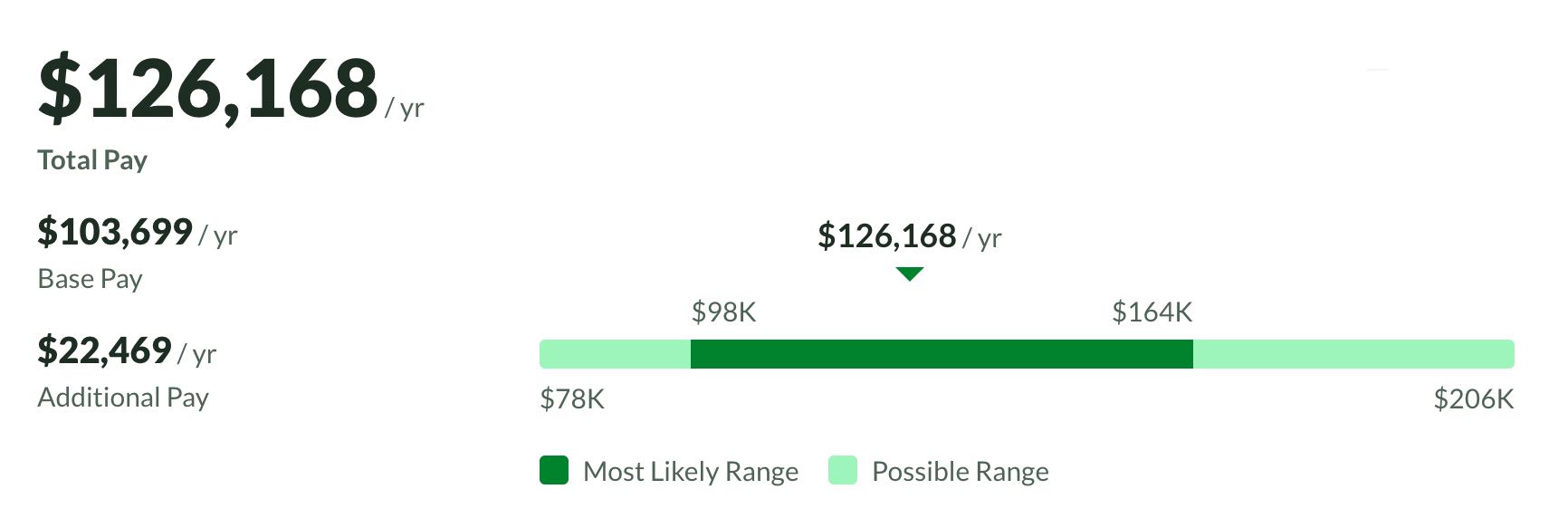
How much does Data Scientist earn
The average salary as a Data Scientist is USD 125,000 per year in New York, USA. The average additional cash compensation for the role of Data Scientist, New York, USA, is US$16,000, ranging from US$5,000 to US$48,000. Salary estimates are based on 3517 salaries submitted anonymously to Glassdoor by employees in a Data Scientist role, New York, USA.
Where to find Data Scientist to do my programming homework
Are you looking for a Data Scientist but don’t know how and where to look for good people for your company? Have you already tried looking through job portals, but in addition to spending time screening CVs and not finding the person you were looking for, have you activated any external providers without satisfactory results? WApart from LinkedIn and Indeed, ee suggest you to check WellFound (former Angel.co), Monster and Infojobs.
Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist
These two professions are increasingly sought after by companies, just as more and more business and science students are winking at specializations in big data, driven not only by the allure of the job but also by the growing employment opportunities and prospects for a good salary.
Both roles have great importance in the areas of market research, competitor analysis, and all those processes of studying data that can significantly determine the success of a company, including yours!
As we said in the introduction, it is a recurring mistake to consider these two professions one and the same, so if you thought this was the case until now, fear not. It is perfectly understandable.
But the reality is that, apart from sharing the word "date," these two jobs require quite distinct skills and competencies.
You will soon find out what they are.
Testifying to this principle are the requirements sought by companies in job descriptions, where these are described in great detail.
By comparing two well-structured job ads in which these two figures are sought, it will be easy and intuitive for you to understand that finding the same knowledge in one figure is conceptually difficult and that they are therefore two separate professions.
Regardless of what a data analyst does and what a data scientist does-a topic we will address in a moment-it is important for you to understand that these two professions do not conflict with each other (as you might mistakenly believe) but rather cooperate within the same area of expertise with specific goals.
Data Scientist vs Data Engineer
Whereas the Data Engineer used to be in charge of data interpretation, the arrival of the Data Scientist has allowed the Data Engineer to focus on the design and maintenance of database systems.
The two figures are thus strongly connected: because of the Data Engineer's work, the Data Scientist has all the tools to be able to produce business models and strategies. There are three types of Data Engineer:
- Architect: is employed in multiple small projects and is responsible for all steps of the data process.
- Database-oriented-man: is employed in larger projects, consequently he can focus on database system management.
- Pipeline-centric-man: employed in medium-sized projects, works closely with the Data Scientist in the data collection process.
- Both figures must have good knowledge in statistics, mathematics and programming, but while the Data Scientist is required to have a good grasp of business dynamics, the Data Engineer's job focuses on devising infrastructure for storing data and devising the best way to transfer it from the source to the recipient.
How to hire a Data Scientist to do my programming homework
According to a study by Linkedin, 75% of talent is passive and already working, not proactively looking for new professional opportunities. Only 25% of them take a more consistent interest in actively searching for new job offers. Consequently, investing the corporate budget in subscriptions and/or offers from job posting platforms certainly cannot be the only effective solution, or at least not the only one.
In fact, the data scientist is one of the professional competence profiles related to digital skills recognised at a European level and became, in January 2016, the subject of a multi-part UNI standard, 11621 1-4, and the summary definition given is as follows:
“…professional figure to whom the activities of collecting, analysing, processing, interpreting, disseminating and visualising quantitative or quantifiable data of the organisation for analytical, predictive or strategic purposes are assigned.”
To select a skilled and professional Data Scientist, we suggest you to look – apart from his CV – at the projects he has already realised or taken part in, preferrably available at GitHub.

Written by Michael Zippo
Michael Zippo, passionate Webmaster and Publisher, stands out for his versatility in online dissemination. Through his blog, he explores topics ranging from celebrity net worth to business dynamics, the economy, and developments in IT and programming. His professional presence on LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/in/michael-zippo-9136441b1/ - is a reflection of his dedication to the industry, while managing platforms such as EmergeSocial.NET and theworldtimes.org highlights his expertise in creating informative and timely content. Involved in significant projects such as python.engineering, Michael offers a unique experience in the digital world, inviting the public to explore the many facets online with him.
